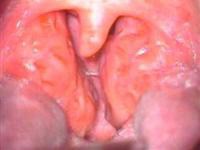
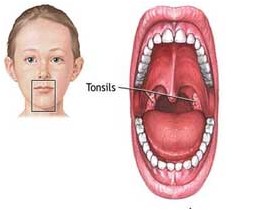
The tonsils are located on each side of the back wall of the throat, just above and behind the tongue. Theses tissues help defend the body against infection. When they are chronically infected or when pus pockets (abscess) developed around it, tonsils may need to be removed. Heavy snoring and cessation of breathing in children could be a warning sign for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome (OSAS). Removal of enlarged tonsils provides dramatic relief and quality of life improvement for these patients.
Who needs the operation?
Recurrent tonsil infections/ strep throat/ peritonsillar abscess
Bad breath or foul taste resulting from chronic tonsillitis
One sided enlargement of tonsil suspicious for cancer in adults
Obstructive sleep apnea in children
Obstructive sleep apnea in adult refractory to CPAP treatment
Tonsil hypertrophy causing trouble swallowing
What is involved with removing the tonsils?
Every patient who is to undergo a tonsillectomy is first screened to make sure there is no increased risk for having excessive bleeding during or after surgery. This is done with a simple questionnaire and possibly some routine blood tests. The surgery is performed through the mouth with the patient under general anesthesia.
Coblation tonsillectomy is the latest technology which has been proven to reduce the amount of postoperative pain after a tonsillectomy.
The procedure lasts about 30 minutes and can usually be performed as an outpatient. Any child with significant medical problems or children under the age of 3 will have to stay in the hospital overnight for observation. Your child will be sent home with prescriptions for an antibiotic as well as for pain medication.
Kevin Ki-Hong Ho, MD
San Francisco
Ear, Nose & Throat Specialist
Golden Gate ENT
Kevin Ki-Hong Ho, MD
San Francisco
Ear, Nose & Throat Specialist
2017 Golden Gate ENT Corp. All rights reserved. Created by Kevin Ho, MD
Kevin Ki-Hong Ho, MD
San Francisco
Ear, Nose & Throat Specialist